ENVIRONMENT
BASIC APPROACH
The Noritsu Koki Group considers climate change one of the social issues it must address as part of its material issues and will work to avoid or reduce the impact of climate change on the Group throughout its entire value chain. To this end, we wii promoting initiatives to contribute to the mitigation of and adaptation to climate change across the entire Group.
INITIATIVES
TARGETS AND PROGRESS
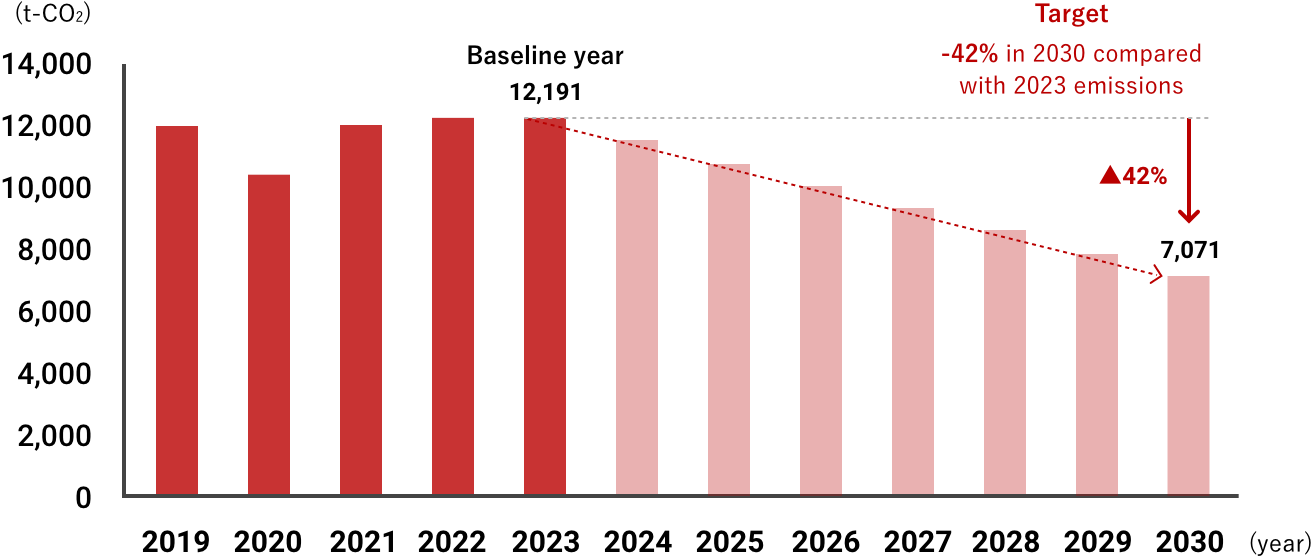
To measure and manage the potential business impact of climate change, using Scope 1 and 2* GHG emissions as our metrics, we have set a target of a 42% reduction by 2030 compared with 2023 (target revised in Sep. 2024). We have reviewed our target to make it aligned with the Science Based Targets initiative’s 1.5℃ scenario.
Performance
| 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scope1 | 1,876 | 1,753 | 2,253 | 2,334 | 1,897 |
| Scope2 | 10,046 | 8,573 | 9,767 | 9,874 | 10,294 |
| Total | 11,923 | 10,325 | 12,020 | 12,208 | 12,191 |
| Emissions(t-CO2) | Percentage | |
|---|---|---|
| Parts/ Materials |
12,076 | 99.1% |
| Audio Equipment/ Peripherals |
83 | 0.7% |
| Others | 32 | 0.3% |
| Total | 12,191 | - |
Please visit here for the Reporting Criteria for 2023 GHG Emission (Scope 1 and 2) in the Integrated Report 2024
- *Emissions for years up to and including 2022 have been restated due to a revision of emission factors and inclusion of gasoline usage in the calculation.
- *Emissions for 2023 have been restated due to a revision of emission factors and inclusion of energy-related CH4, N2O and other non-energy-related GHGs in the calculation.
- *The Scope 1 and 2 GHG emissions for 2023 disclosed in the Integrated Report 2024 have been assured by the third party organization.Please refer to page 35, 57 and 58 of the Integrated Report 2024.
- *Scope 1: Direct emissions from a company’s business (fuel consumption, industrial processes, etc.)
Scope 2: Indirect energy-related emissions from electric power and other energy consumed by a company
IMPLEMENTING SCOPE 1 AND 2 REDUCTION PLAN
At Teibow Group*, which has its own manufacturing sites, solar power generation equipment was installed at two of its domestic sites. In addition, the company focuses on reducing energy usage by introducing energy-saving equipment, streamlining production processes and promoting technological innovation. At AlphaTheta, the company continues to use 100% green electricity at the building that houses its head office.
- *Teibow Holdings, Teibow and its subsidiaries, and Hamamatsu Metal Works

CALCULATING SCOPE3 EMISSIONS
In 2023 we have started calculating Scope 3* emissions. We will continue considering ways to reduce GHG emissions throughout our entire supply chain.
- *Scope 3: Indirect emissions other than Scope 1 and 2 (emissions by others in the upstream and downstream of a company’s activities)
Scope 3 Emissions (2023)
| Category | Emissions(t-CO2) | Percentage | Calculation Summary |
|---|---|---|---|
|
01
Purchased goods and services
|
178,094 | 60.2% | Emissions associated with raw materials, parts, and purchased products/services |
|
02
Capital goods
|
6,175 | 2.1% | Emissions generated by the capital investment |
|
03
Fuel-and energy-related activities not included in Scope1 and 2
|
2,045 | 0.7% | Emissions associated with energy procurement |
|
04
Upstream transportation and distribution
|
9,473 | 3.2% | Emissions associated with transportation of raw materials and products (including outbound logistics owned by the Group ) |
|
05
Waste generated in operation
|
546 | 0.2% | Emissions associated with waste from business activities |
|
06
Business travel
|
150 | 0.1% | Emissions associated with employees’ business travel |
|
07
Employee commuting
|
220 | 0.1% | Emissions associated with employees’ commuting |
|
08
Upstream leased assets
|
- | - | Not applicable |
|
09
Downstream transportation and distribution
|
1,723 | 0.6% | Emissions associated with transportation of raw materials and products |
|
10
Processing of sold products
|
- | - | Not applicable |
|
11
Use of sold products
|
96,581 | 32.7% | Emissions associated with expected electricity consumption by products sold |
|
12
End-of-life treatment of sold products
|
731 | 0.2% | Emissions associated with expected disposal of products sold |
|
13
Downstream leased assets
|
- | - | Not applicable |
|
14
Franchises
|
- | - | Not applicable |
|
15
Investments
|
- | - | Not applicable |
| Total | 295,740 |
DISCLOSURE BASED ON THE TCFD RECOMMENDATIONS
The Noritsu Koki Group expressed its support for the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) recommendations in October 2022. Guided by the recommendations, we will identify the potential business implications of climate-related risks and opportunities and reflect them in our business strategy. We are committed to information disclosure and ensuring the realization of a sustainable society as well as the Group’s sustainable growth.
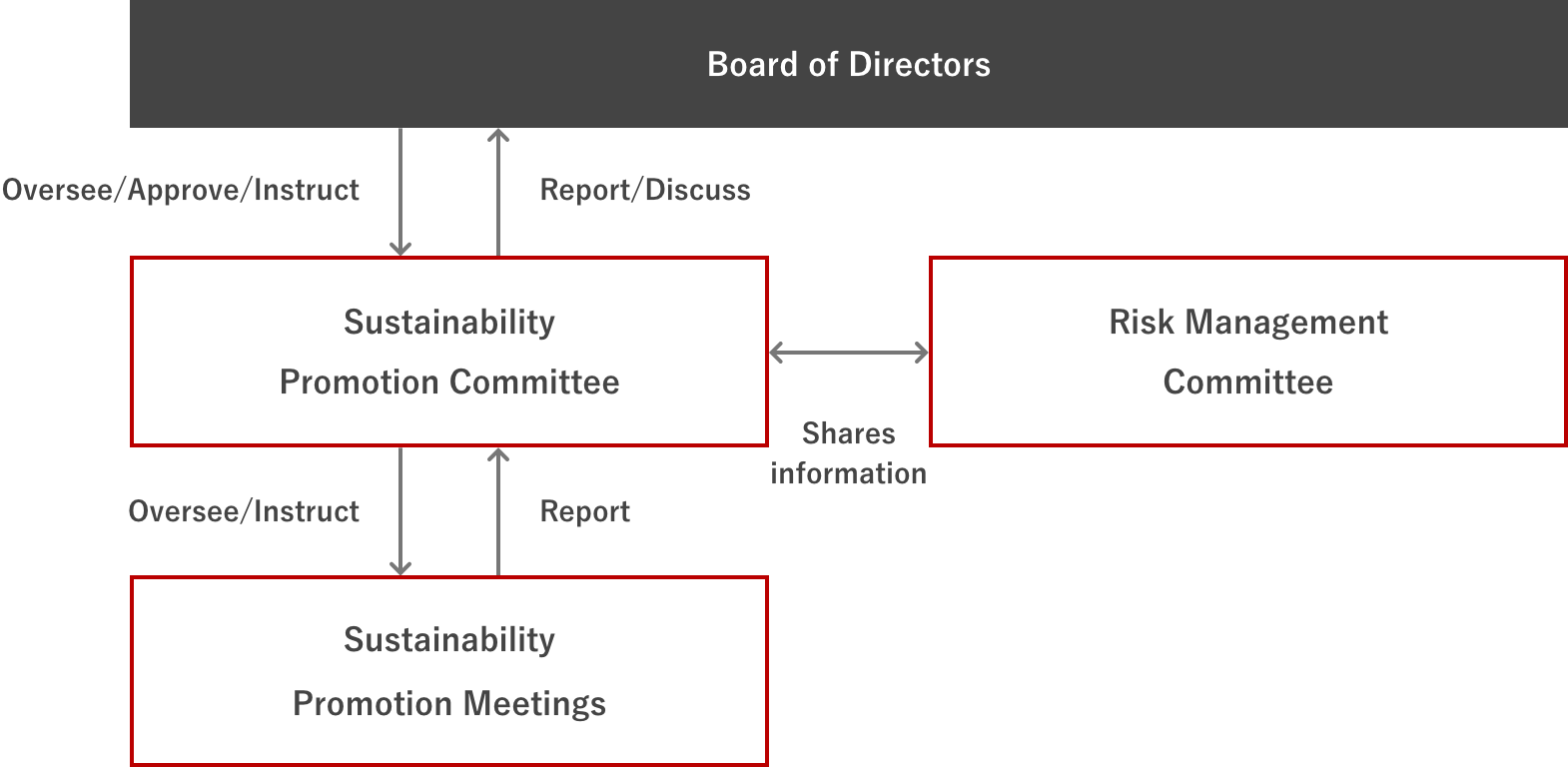
GOVERNANCE : ROLE OF THE BOARD OF DIRECTORS AND MONITORING SYSTEM
The Group’s Sustainability Promotion Committee, chaired by the representative director and CEO of Noritsu Koki, deliberates at least once a year on important sustainability issues including climate change responses. It also provides reports and recommendations to the Board at least four times a year, thereby ensuring an appropriate monitoring system. The Board deliberates and makes decisions on important climate-related risks and opportunities, and also provides direction and oversees progress.
Prior to the deliberations of the Sustainability Promotion Committee, important sustainability issues are first thoroughly discussed in Sustainability Promotion Meetings chaired by an executive officer. In the meetings, members share the results of initiatives to address climate change through business activities and efforts to reduce GHG emissions throughout the Group.
RISK MANAGEMENT : RISK ASSESSMENT, IDENTIFICATION AND MANAGEMENT PROCESS
The Sustainability Promotion Committee assesses, analyzes and identifies climate-related risks and opportunities that may significantly impact the Group and its business. The committee develops policies and measures to mitigate these risks and take advantage of opportunities. It also presents reports and recommendations to the Board of Directors. The Board oversees the effectiveness of the risk management process and overall progress.
The Risk Management Committee manages overall risks across the entire Group. It shares information on climate change-related risks with the Sustainability Promotion Committee and considers further action as appropriate.
| Responsible Parties | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Board of Directors |
|
| Sustainability Promotion Committee |
|
| Risk Management Committee |
|
| Sustainability Promotion Meetings |
|
STRATEGY : SCENARIO ANALYSES
To strengthen the Group’s resilience, respond to risks and opportunities that may impact business and develop new strategies, we performed scenario analyses. We used the 1.5℃–2℃ scenario and the 4℃ scenario as presented by organizations such as the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) and the International Energy Agency (IEA). In the scenario analyses we identified two types of risks: transition risks, which are related to tightening of policies and regulations with the transition to a decarbonized society, and physical risks, which are associated with the increasing severity of abnormal weather events and a rise in average temperatures. Based on quantitative analyses, we assessed the possible financial impact by 2030.
Noritsu Koki recognizes the potential for climate change issues to have a significant impact on the Group’s businesses, strategies and financial plans. We therefore regularly assess risks and opportunities and revise our strategies.
| Adopted Scenarios |
1.5℃scenario |
|
|---|---|---|
| 2℃scenario |
|
|
| 4℃scenario |
|
OUR RESPONSES TO CLIMATE-RELATED RISKS AND OPPORTUNITIES
Timeframe: Up to 2030
Financial impact assessment indicators: Small (less than ¥500 million) / Medium (from ¥500 million to less than ¥3 billion) / Large (¥3 billion or more)
| Risk type | Scenario | Financial Impact |
Group Response | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TRANSITIONRISK | Policies and regulations | Risk |
|
Small |
|
| Risk |
|
Small | |||
| Risk |
|
Small | |||
| Technology | Risk |
|
Medium |
|
|
| Market | Risk |
|
Medium |
|
|
| Opportunity |
|
Medium | |||
| Reputation | Opportunity |
|
Small |
|
|
| PHYSICALRISK | Acute | Risk |
|
Small* |
|
| Chronic | Risk |
|
Small |
|
|
- *For acute physical risks, we assessed domestic Group sites using hazard maps, flood control economic survey manuals and other tools. Under the 4°C scenario, one site would be at risk for business suspension and asset losses due to disasters. Given the recurrence period, however, the annual impact is low. We have therefore classified the impact as “small.” Going forward, we will continue to evaluate the impact, including at contract manufacturer sites.
METRICS AND TARGETS
To measure and manage the potential business impact of climate change, using Scope 1 and 2* GHG emissions as our metrics, we have set a target of a 42% reduction by 2030 compared with 2023 (target revised in Sep. 2024). We have reviewed our target to make it aligned with the Science Based Targets initiative’s 1.5℃ scenario. In addition, in 2023 we have started calculating Scope 3* emissions (disclosed in CDP Response 2024) . We will continue considering ways to reduce GHG emissions throughout our entire supply chain.
Performance
| Results | Targets | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2030 | |
| Scope1・2 | 11,923 | 10,325 | 12,020 | 12,208 | 12,191 | 7,071 |
Please visit here for the Reporting Criteria for 2023 GHG Emission (Scope 1 and 2) in the Integrated Report 2024
- *Emissions for years up to and including 2022 have been restated due to a revision of emission factors and inclusion of gasoline usage in the calculation.
- *Emissions for 2023 have been restated due to a revision of emission factors and inclusion of energy-related CH4, N2O and other non-energy-related GHGs in the calculation.
- *The Scope 1 and 2 GHG emissions for 2023 disclosed in the Integrated Report 2024 have been assured by the third party organization.Please refer to page 35, 57 and 58 of the Integrated Report 2024.
- *Scope 1: Direct emissions from a company’s business (fuel consumption, industrial processes, etc.)
Scope 2: Indirect energy-related emissions from electric power and other energy consumed by a company
Scope 3: Indirect emissions other than Scope 1 and 2 (emissions by others in the upstream and downstream of a company’s activities)